Ultrasonic Welding/Gluing
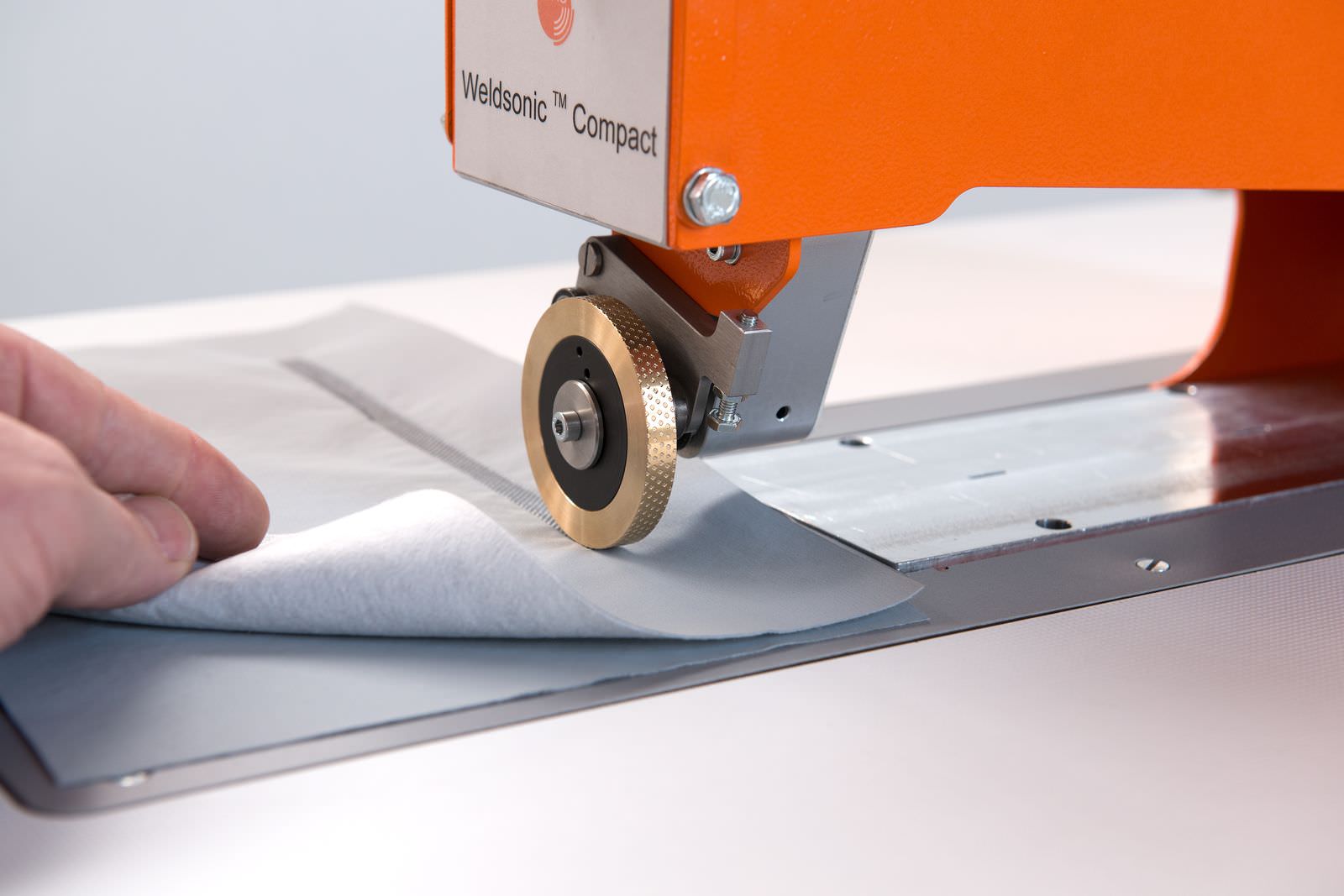

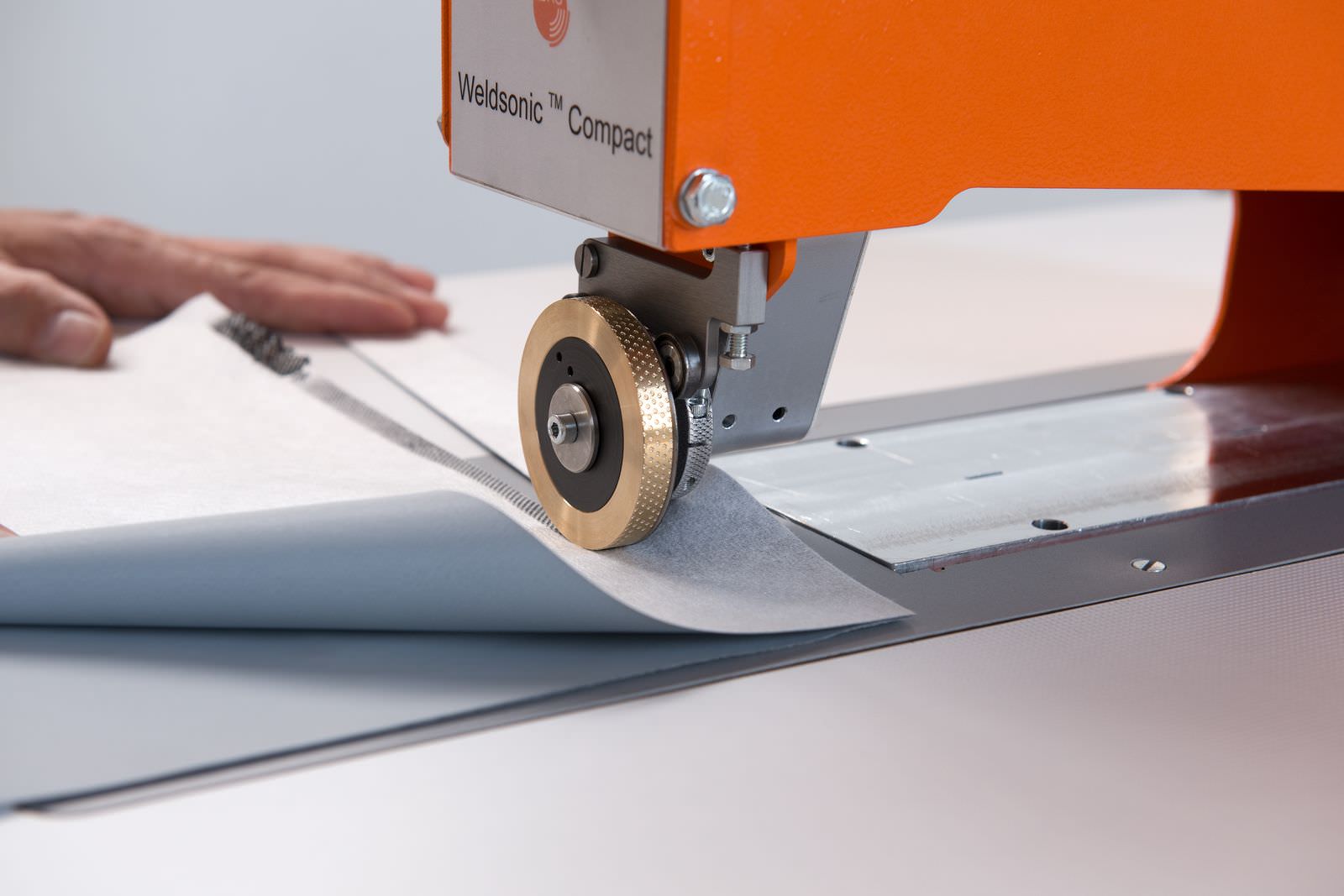
Jentschmann A.G. uses 35 kHz ultrasound technology to bond technical textiles. This application is called ultrasonic welding or ultrasonic bonding.
But how does ultrasound and the ultrasonic welding process actually work?Ultrasound is defined as sound at frequencies from about 16 kHz to 1 Ghz – i.e. mechanical vibrations in the range of 16,000 times per second and up.
Generating ultrasound requires 3 components: an ultrasonic generator, a sound unit (consisting of a converter and optionally a booster ), and an ultrasonic horn.
The ultrasonic generator creates a high frequency electrical signal which is transmitted by a specially shielded high frequency cable to the converter. The converter is a piezoelectric ceramic which vibrates in response to the electrical signal (called a transducer because it converts the electrical oscillation into a mechanical one). The booster (if used) increases the amplitude of vibration and transfers the mechanical vibrations to the horn (also referred to as sonotrode).
The energy that is required for ultrasonic welding is created by transferring the vibrations from the horn to the material to be welded under pressure. This causes the molecules in the material to vibrate, resulting in heat.
This heat is used in the ultrasonic bonding process, either for direct bonding (ultrasonic welding) or for melting a hot melt adhesive (ultrasonic gluing) which joins the material together under pressure.
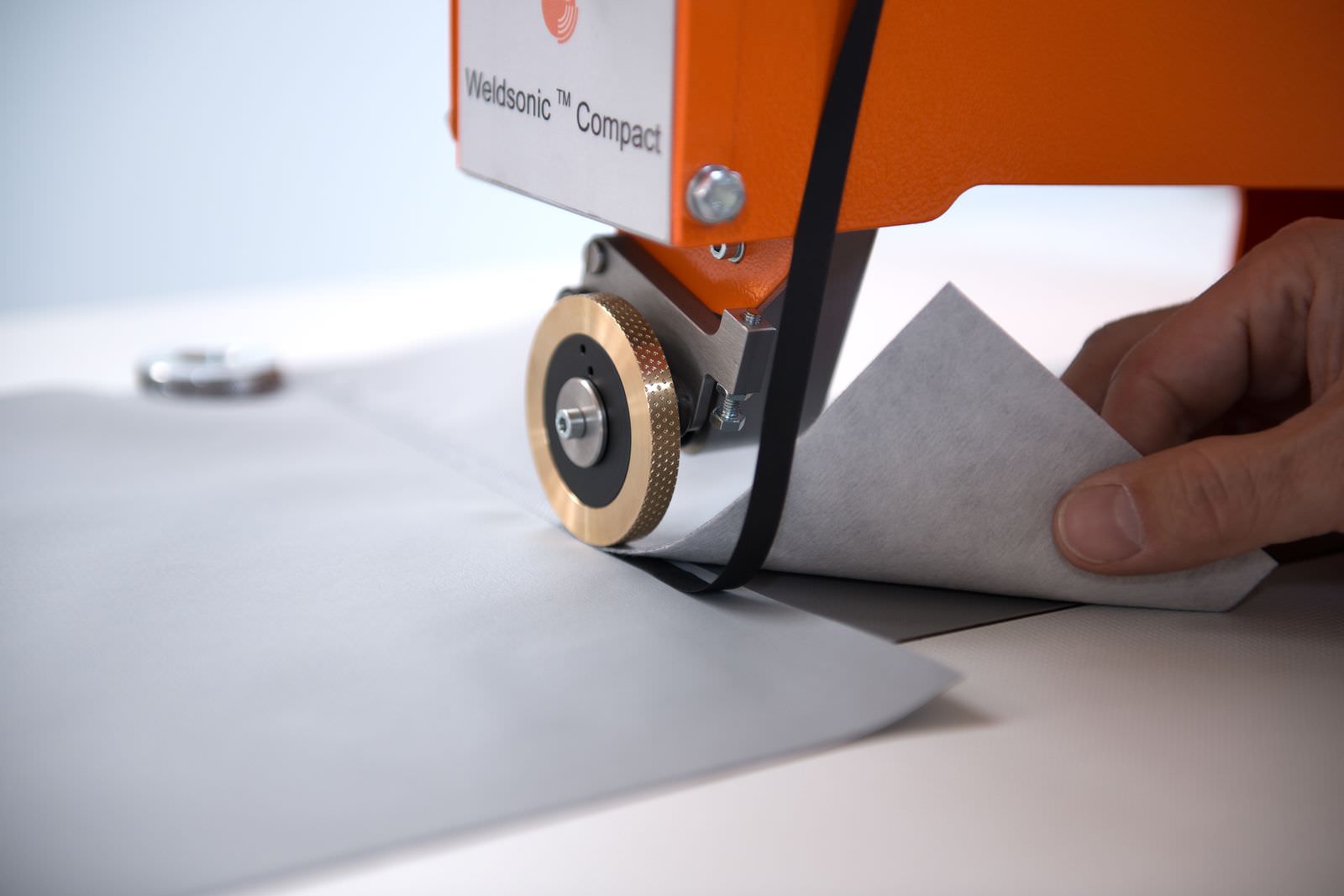
Jentschmann A.G. has developed a sophisticated ultrasonic rotating sonotrode (horn). This rotary ultrasonic welding method has the advantage that the technical textiles can be welded continuously. This achieves higher processing speed and avoids the seam gaps or overlaps which occur with stationary sonotrodes.
Since the Jentschmann rotary sonotrode is a wheel the material feeding is consistent across the entire width of the weld – unlike vertically oriented rotating disk technology.
When welding with the Jentschmann ultrasonic rotary technology the vibrations of the rotary horn are transfered through the material to be welded and then reflected onto an anvil. The anvil wheel exerts the necessary pressure to weld the material and also creates the desired seam design.
The Jentschmann ultrasonic welding system is designed so that the rotary horn and the anvil wheels both have their own variable speed drive.
For accurate ultrasonic welding, the speed ratio of the rotary horn to the anvil wheel can be adjusted according to the material to be welded. This prevents the material layers from shifting and guarantees a uniform flat seam without waves and wrinkles from the beginning to the end.
Applications
-
ScreenSonic360
Ultrasonic gluing machine for all typical edge operations including TRail and joining…
-
Weldsonic™ Twin 4.0
Ultrasonic gluing machine for joining, hemming, applying ZIP and different edge operations…
-
Weldsonic™ Blind
Weldsonic™ Blind The Weldsonic™ Blind is designed to apply edge tapes or…
-
Weldsonic™ Filter
Weldsonic™ Filter The Jentschmann Weldsonic™Filter is an ultrasonic welding machine for continuous…
-
Weldsonic™ Solo
Weldsonic™ Solo The Jentschmann Weldsonic™ Solo is a stand-alone flatbed Ultrasonic welding…